Introduction
Integrated project performances play a crucial role in Kuwait's development plan, providing public clients with practical solutions. This research presents norms in three categories, focusing primarily on delivery performance during the construction phase. A quantitative method was adopted, utilizing paper-based and online questionnaire surveys to gather primary data. The study investigates infrastructure provision through various integrated schemes, including PPP, BOT, and BOOT models.
Data Collection and Analysis
After data collection, responses from 272 out of 375 public sector participants and 79.01% private sector participants were analyzed. A statistical analysis was conducted to evaluate cost and time performance across different project types. The methodology involved using spreadsheets and survey tools like Survey Monkey to assess the collected data. Projects were categorized into four types, and a Relative Percentage Change (RPC) equation was applied to measure delivery performance variations.
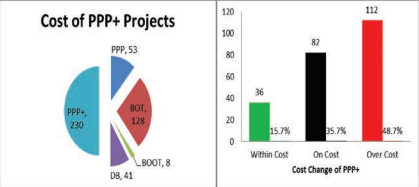
Cost Performance Findings
- PPP Projects: 41.5% within cost, 37.7% on cost, 20.8% over cost.
- BOT Projects: 7% within cost, 35.9% on cost, 57.1% over cost.
- BOOT Projects: 75% on cost, 25% over cost, 0% within cost.
- DB Projects: 12.2% within cost, 24.4% on cost, 63.4% over cost
Findings indicate that PPP and BOOT models are cost-efficient, while DB projects frequently exceed costs.
Time Performance Findings
- PPP Projects: 62.7% on time, 21.6% over time.
- BOT Projects: 47.2% on time, 43.3% over time.
- BOOT Projects: 80% on time, 20% over time.
- DB Projects: 36.6% on time, 61% over time.
Results suggest PPP and BOOT projects maintain better time efficiency, whereas DB projects experience significant delays.
Implications for Kuwait’s Infrastructure Development
Findings emphasize the importance of integrated project models for Kuwait's infrastructure growth:
- PPP projects attract investors with balanced cost-time efficiency.
- BOOT projects provide long-term stability.
- DB projects need improved cost and time management strategies.
Conclusion and Future Work
This study supports increased private sector involvement in PPP and BOOT projects for Kuwait's infrastructure development. Future research should explore policy enhancements, risk management, and regulatory improvements to optimize project performance.
